New Map of Insulin Pathway Could Lead to Better Diabetes Drugs
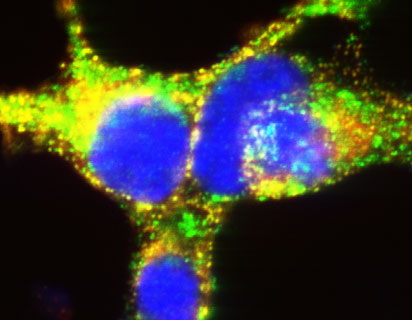
A team led by the Balch lab has created the first comprehensive roadmap of the protein interactions that enable cells in the pancreas to produce, store and secrete the hormone insulin.

Scientists Develop New Process to Create Artificial Cell Membranes
Preparing synthetic versions of cell membranes has been a long-standing challenge—but a new method from the Paegel lab may change that.
Researchers Shed Light on Body’s Master Energy Regulator
The new discoveries from the Griffin lab could help in the design and development of new therapeutics to treat metabolic disease such as diabetes and obesity, and perhaps some cancers.
Study Finds New Moves in Protein’s Evolution
The research, led by the Wright lab, points to a new approach to drug design.